L-FABP Research Use Kit for animals
Intended animals: Rat, Dog, Monkey, Cat, Pig
- 【Rat】Rat L-FABP ELISA Kit (Part Number 008)
- 【Dog】Canine L-FABP ELISA HS Kit (Part Number 009)
- 【Monkey】Primate L-FABP ELISA Kit (Part Number 010)
- 【Cat】Feline L-FABP ELISA HS Kit (Part Number 011)
- 【Pig】Porcine L-FABP ELISA Kit (Part Number 012)
This is ELISA kit for colorimetric analysis on urinary L-FABP (L-Fatty Acid Binding Protein) by 2-step sandwich method.
※For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
※This product is developed by CMIC HOLDINGS Co., Ltd.
This product received Technical Awards at Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Toxicology in 2015. It has
received an attention as a marker for drug-induced nephropathies of animals.
※Suzuki et al. Comparison of time course of urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP)
and other urinary nephrotoxicity biomarkers of drug-induced acute kidney injury in rats, 2015.
What is urinary L-FABP?
L-FABP is a soluble protein of 14 kDa in molecular weight, and specifically expressed in proximal tubule inside the kidney. In a physiological way, L-FABP plays an important role in energy and lipid metabolism at renal tubule, which takes on the function of reabsorption inside the kidney. The conventional urinary markers are excreted into urine due to tissue failure of glomerulus and renal tubule. L-FABPs, on the other hand, are excreted into urine due to ischemia or inadequate blood flow, andoxidant stress on renal tubule before the progression of tissue failure. Therefore, L-FABP is considered as useful biomarker for early diagnosis of renal disease accompanying tubular dysfunction.
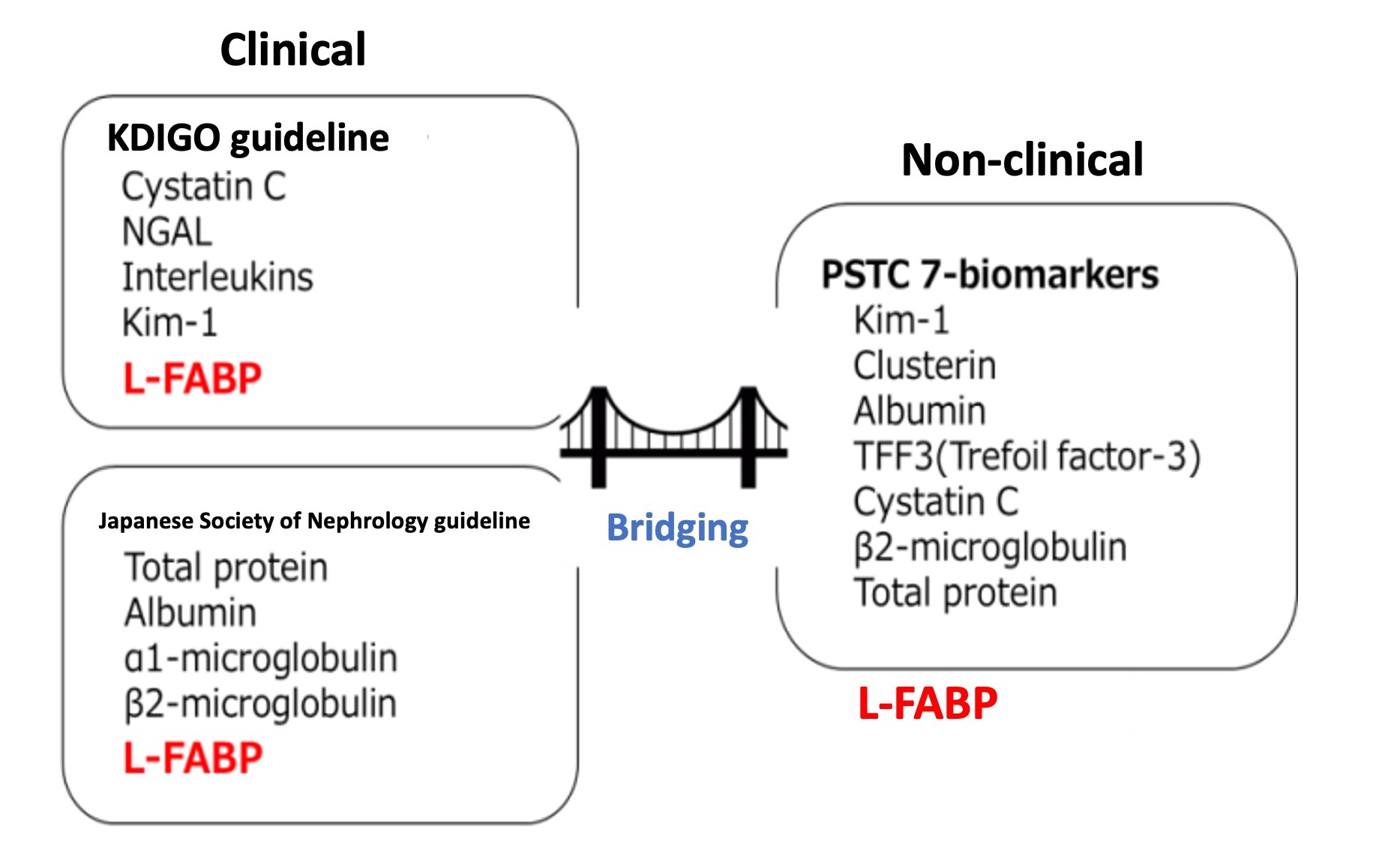
Human L-FABP was approved by Japanese MHLW in August 2011, and already integrated into clinical practice as a biomarker.
L-FABP is explicitly stated in KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcome) international guideline, and in the guide line for chronic kidney disease published by Japanese Society of Nephrology guideline. As well as research interest, L-FABP has gained social recognition as promising urinary biomarker for diagnosis of kidney disorder and the prognosis prediction.
In contrast, L-FABP has not been nominated as the non-clinical kidney biomarker recommended by PSTC (The Predictive Safety Testing Consortium). L-FABP can be a bridge between clinical field and non-clinical field and that should be endorsed by future studies.
Characteristics: Technical development for High Sensitivity ELISA assay enables user to measure L-FABP in animal urine

- Advantageous in sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility
- Measurement Sample: Animal urine
- Measurement Method: enzyme immunometric assay (Sandwich ELISA Method)
- Measurement Wavelength: 450nm (reference wavelength: 610nm or over)
- Assay time: about 3 hours
- Intended animals: Rat, Dog, Monkey, Cat, Pig
Example: Rat L-FABP ELISA Kit (Part Number 008)
1. Change of urinary L-FABP in each drug-induced renal injury model
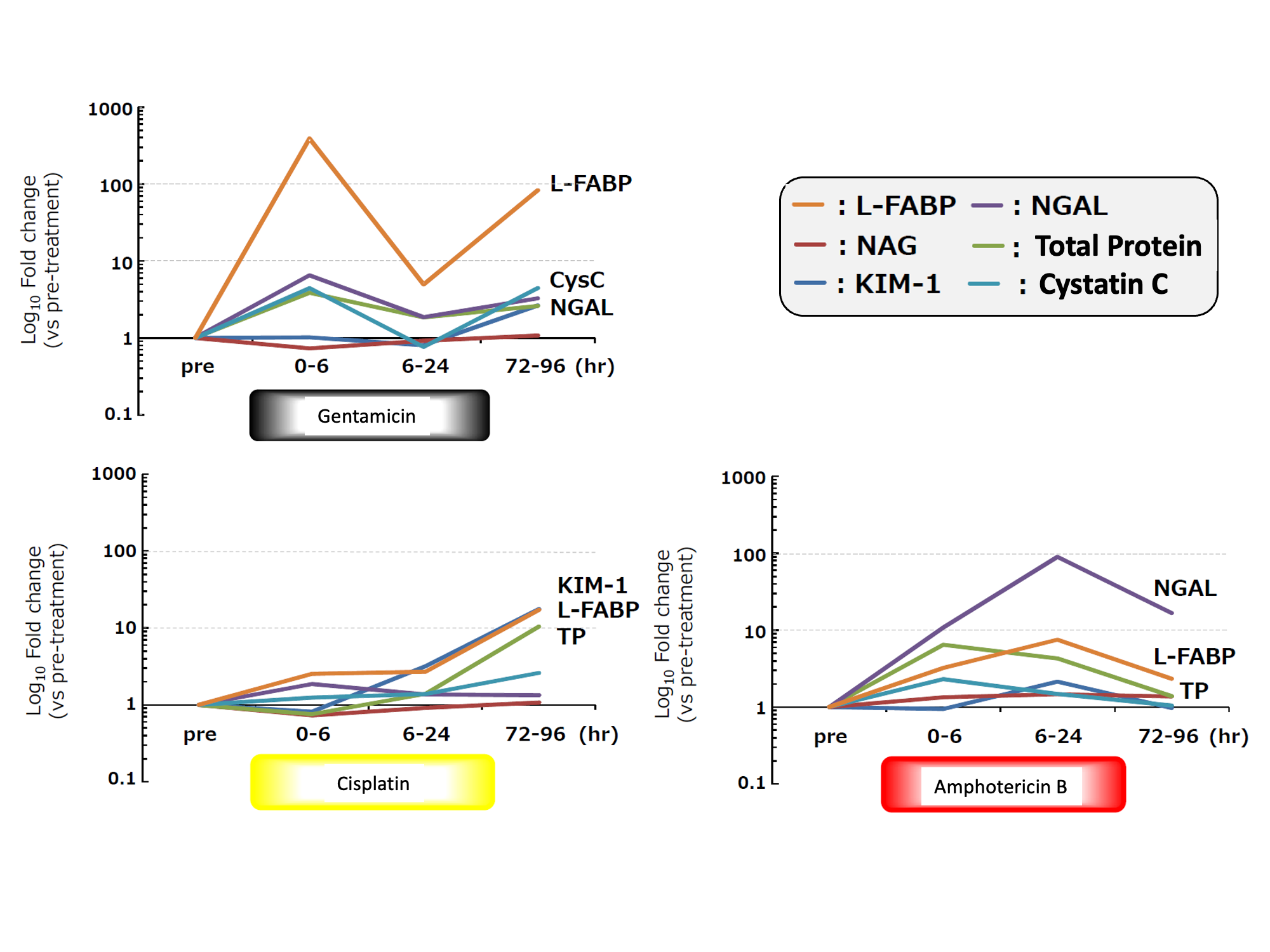
Test animal: 6 weeks age male SD rat
Administered drug:
- Gentamicin (200mg/kg, subcutaneous administration)
- Cisplatin (4mg/kg, intravenous administration)
- Amphotericin B (50mg/kg, intraperitoneal administration)
Method:
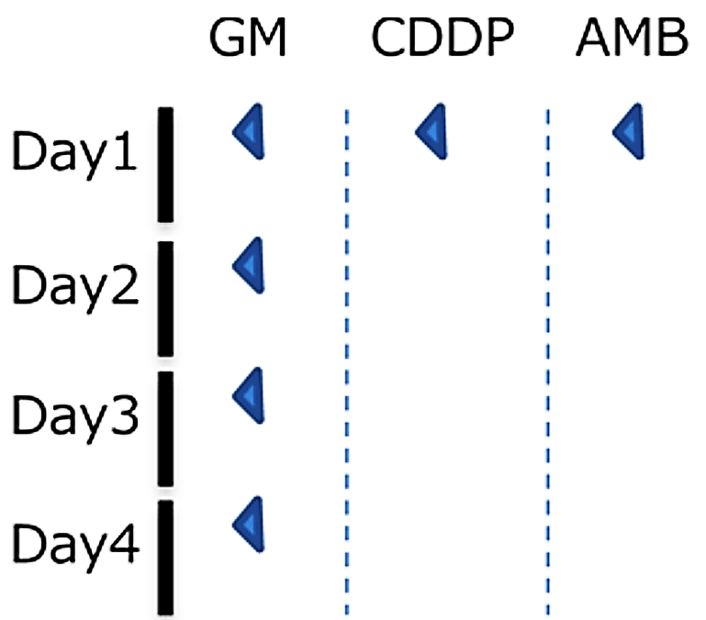
2.Change of urinary L-FABP in Gentamicin renal injury model rat
- Test animal: 6 weeks age male SD rat
- Administered drug: Gentamicin (200mg/kg/day, subcutaneous administration)
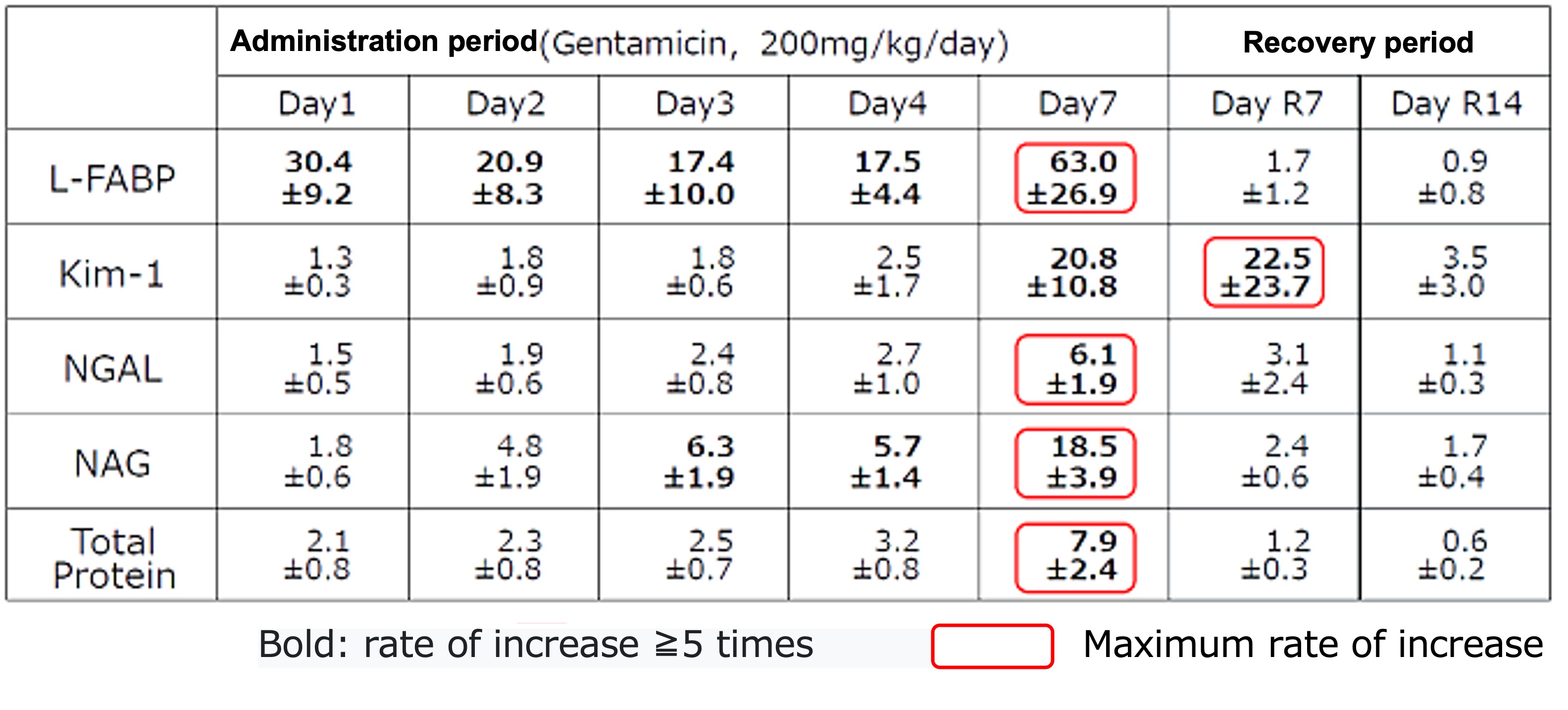
- Method: After administrating Gentamicin 7 days in a row, collected urine and measured each urinary biomarker as the below:
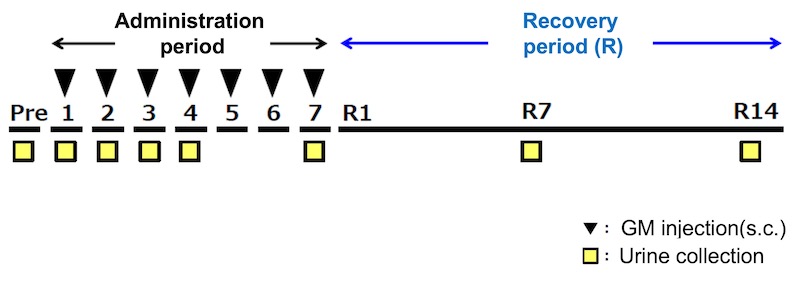
Relative fold change of each urinary biomarker relative to the control at every sampling point
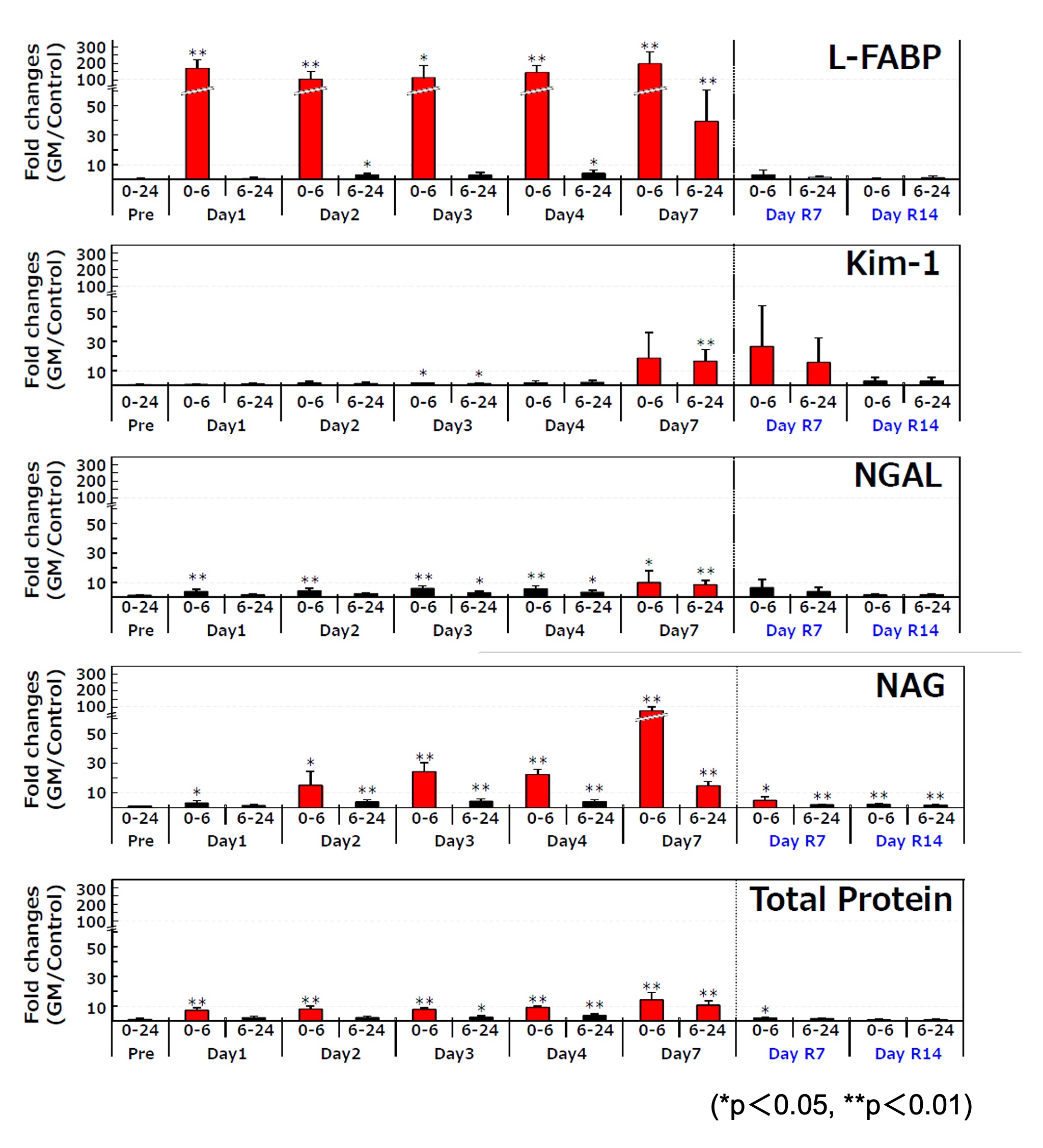
Change ratio of each urinary biomarker
Mean±S.D., n=6
Level of urinary L-FABP
- elevated in an early stage (within 6 hours) after administrating Gentamicin
- elevated every time after administrating Gentamicin
- showed the highest change ratio
- lowered to the same level as control group in recovery period
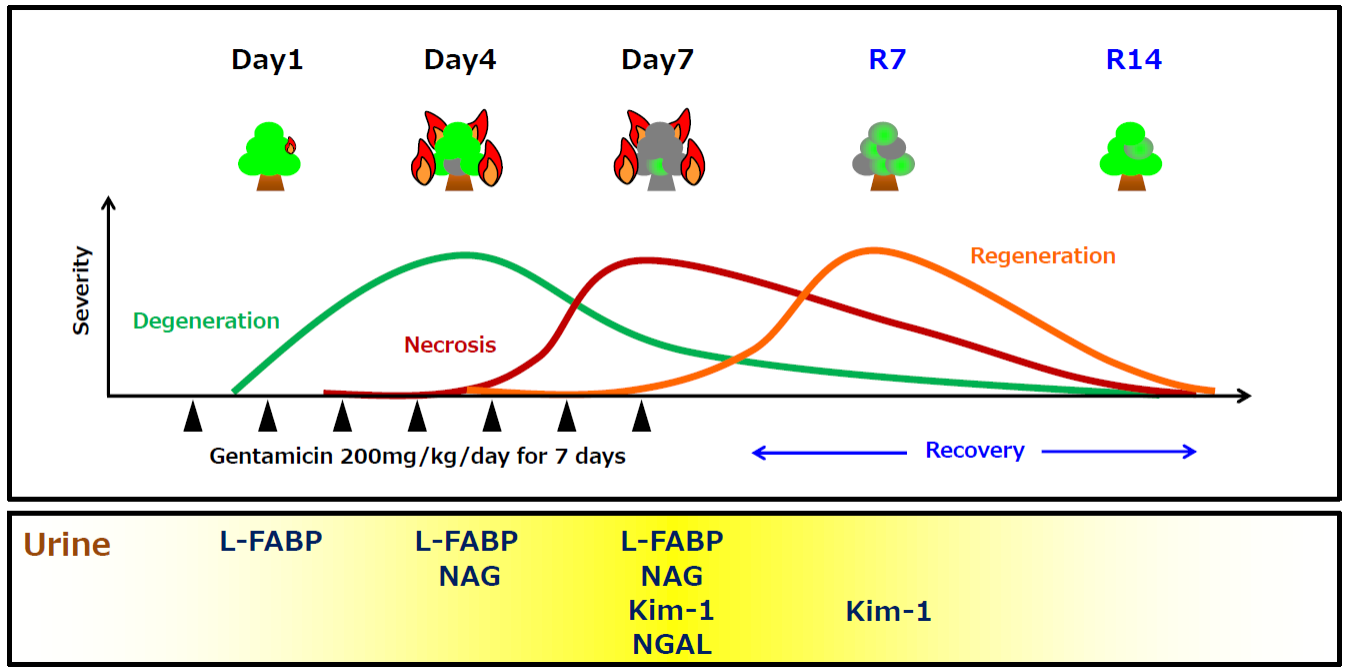
Relation between proximal tubular dysfunction and each urinary biomarker
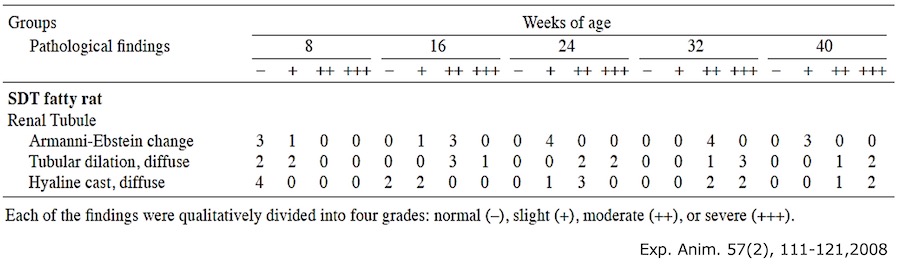
3. Urinary L-FABP measurement of Type 2 diabetes model rat・SDT fatty rat*
- Test animal: male SDT fatty rat*, male SD rat (control)
- Method: Urine samples of SDT fatty rat and SD rat were collected at 8, 16, and 24 weeks of age. Urinary L-FABP and creatinine were measured.
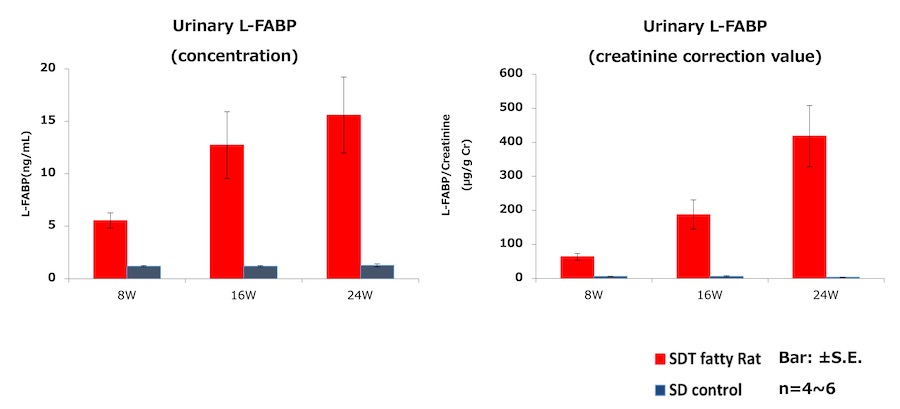
Result:Urinary L-FABP showed high level at 8 weeks of age, when a renal tubular lesion is disclosed.
*about SDT fatty rat
It is the spontaneous type 2 diabetes model rat produced and sold by CLEA Japan, Inc. It has human-resembled characteristics in symptoms, such as nodular glomerular lesion, which is unique to human diabetic nephropathy. Hence application is suggested for CKD pathological analysis and therapeutic drug development. It shows decrease of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) around 18 weeks of age by undergoing unilateral nephrectomy and salt water supplement, thus it enables pathological control tailored to the experiments. As the table below, renal tubular disorders are acknowledged from around 8 weeks of age.